9th Mahts 6.3
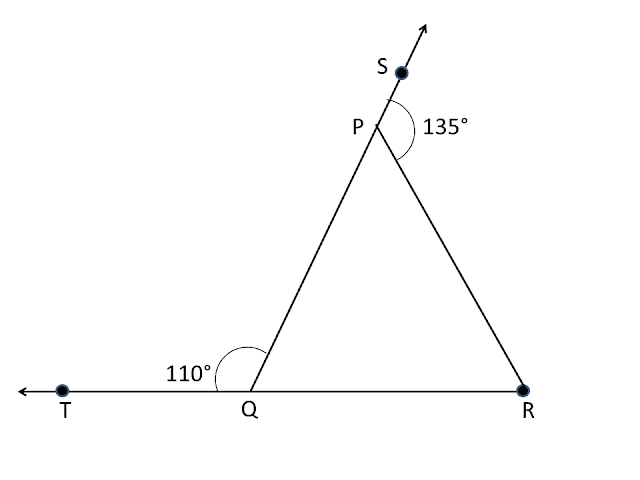
NCERT Class 9th solution of Exercise 6.1 NCERT Class 9th solution of Exercise 6.2 Exercise 6.3 Q1. In the given figure, sides `QP` and `RQ` of `△PQR` are produced to points `S` and `T` respectively. If `∠SPR=135°` and `∠PQT=110°`, find `∠PRQ`. Sol. `∠PQT+∠PQR=180°` [ By linear pair. ] `110°+∠PQR=180°` [ Given `∠PQT=110°` ] `∠PQR=180°-110°` `∠PQR=70°` `∠PRQ+∠PQR=∠SPR` [ By exterior angle property ] `∠PRQ+70°=135°` [ Given `∠SPR=135°` ] `∠PRQ=135°-70°` `∠PRQ=65°` Answer : The required value of `∠PRQ=65°`. Q2. In the given figure, `∠X=62°, ∠XYZ=54°`. If `YO` and `ZO` are the bisectors of `∠XYZ` and `∠XZY` respectively of `△XYZ`, find `∠OZY` and `∠YOZ`. Sol. : In `△XYZ`, `∠YXZ+∠XYZ+∠XZY=180°` ...