10th Maths 8.1
Chapter 8
Introduction to Trigonometry
Subscribe to Quiz10 for Important MCQs
NCERT Class 10th solution of Exercise 8.2
NCERT Class 10th solution of Exercise 8.3
NCERT Class 10th solution of Exercise 8.4
Exercise 8.1
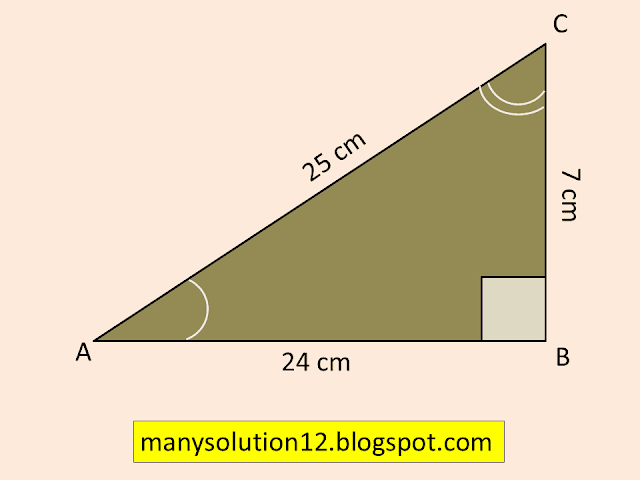
Q1. In `triangle ABC`, right-angled at `B`, `AB=24 cm, BC=7 cm`. Determine:
i) sin `A`, cos `A`
ii) sin `C`, cos `C`.
Sol. :
By Pythagoras theorem
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`AC^2 = (24)^2+(7)^2`
`AC^2 = 576 + 49`
`AC^2 = 625`
`AC^2 = (25)^2`
`AC = 25 cm`
i)
`sin A = (BC)/(AC) = 7/25`
`cos A = (AB)/(AC) = 24/25`
Answer:
`sin A = 7/25, cos = 24/25`
ii)
`sin C = (AC)/(AC) = 24/25`
`cos C = (BC)/(AC) = 7/25`
Answer:
`sin C = 24/25, cos C = 7/25`
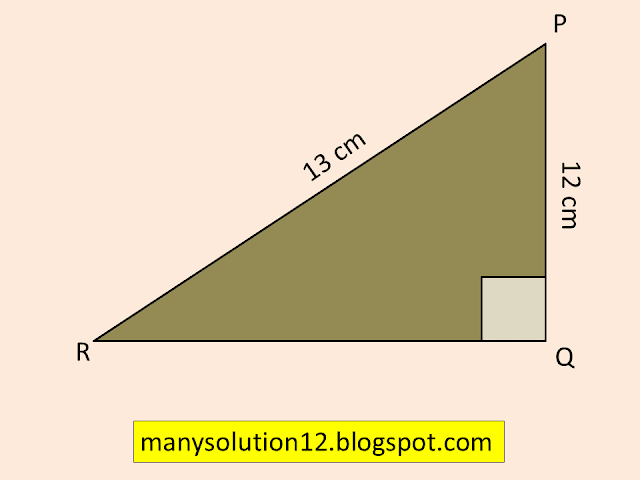
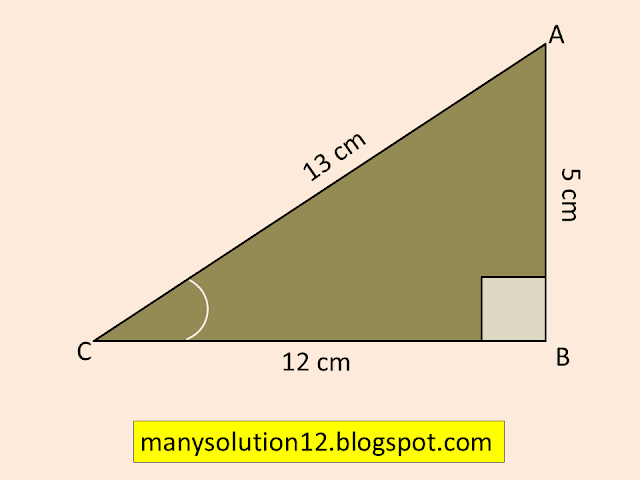
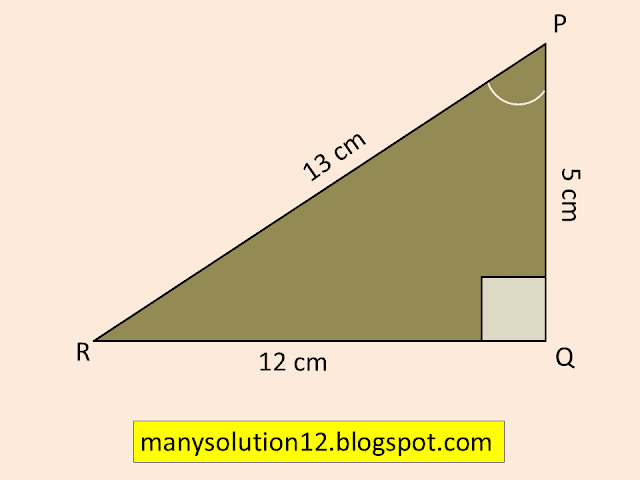
Q2. In figure, find `tanP-cotR.`
In `triangle PQR,`
By Pythagoras theorem
`QR^2 = PR^2 - PQ^2`
`QR^2 = (13)^2 - (12)^2`
`QR^2 = 169 - 144`
`QR^2 = 25`
`QR^2 = (5)^2`
`QR = 5 cm`
`= tan P - cot R`
`= (QR)/(PQ) - (QR)/(PQ)`
`= 5/12 - 5/12`
`= 0`
Answer:
`tan P - cot R = 0.`
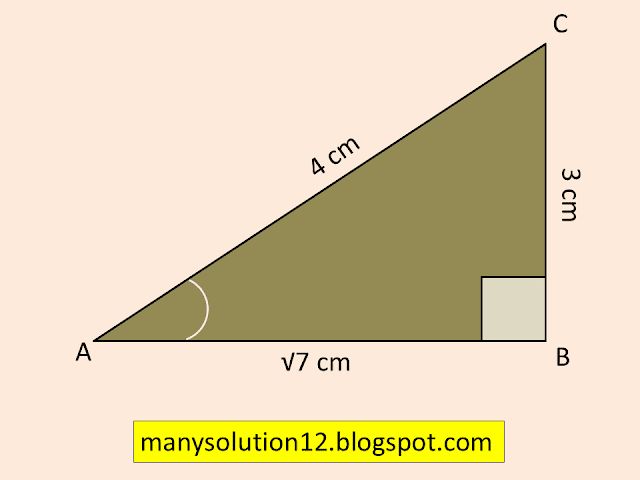
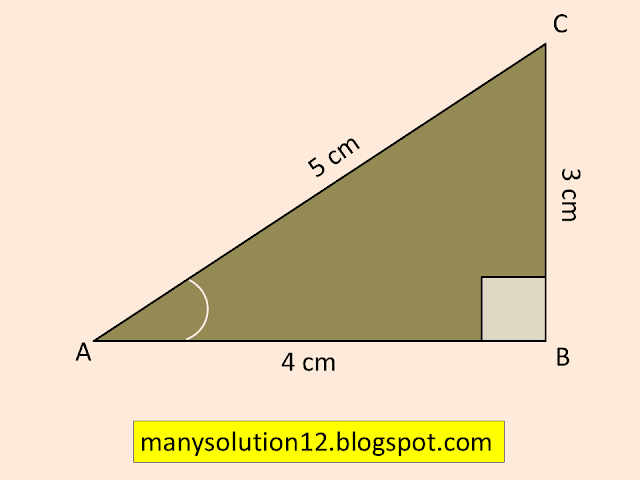
Q3. If `sin A=3/4,` calculate `cos A` and `tan A.`
Sol. :
`sin A = 3/4`
To Find:
`cos A, tan A`
Solve:
In `triangle ABC, angle B = 90^circ`
`sin A = 3/4 = (BC)/(AC)`
By Pythagoras theorem
`AB^2 = AC^2 - BC^2`
`AB^2 = (4)^2 - (3)^2`
`AB^2 = 16 - 9`
`AB^2 = 7`
`AB = sqrt7`
`cos A = (AB)/(AC) = (sqrt7)/4`
`tan A = (BC)/(AB) = 3/(sqrt7)`
Answer:
`cos A = (sqrt7)/4, tan A = 3/(sqrt7)`
Q4. Given `15 cot A=8,` find `sin A` and `sec A`.
Sol. :
`cot A = 8/15`
To find:
`sin A` and `sec A`.
Solve:
In `triangleABC`
`cot A = 8/15 = (AB)/(BC)`
By Pythagoras theorem
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`AC^2 = (8)^2 + (15)^2`
`AC^2 = 64 + 225`
`AC^2 = 289`
`AC^2 = (17)^2`
`AC = 17`
`sin A = (BC)/(AC) = (15)/(17)`
`sec A = (AC)/(AB) = (17)/8`
Answer:
`sin A = (15)/(17)` and `sec A = (17)/8`.
Q5. Given `sec theta=13/12,` calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
Sol. :
`sec theta = 13/12`
To Find:
All trigonometric ratios.
Solve:
In `triangle ABC`
`sec theta = 13/12 = (AC)/(BC)`
By Pythagoras theorem
`AB^2 = AC^2 - BC^2`
`AB^2 = (13)^2 - (12)^2`
`AB^2 = 169 -144`
`AB^2 = 25`
`AB^2 = (5)^2`
`AB = 5`
`sin theta = (AB)/(AC) = 5/12`
`cos theta = (BC)/(AC) = 12/13`
`tan theta = (AB)/(BC) = 5/12`
`cosec theta = (AC)/(AB) =13/5`
`cot theta = (BC)/(AB) = 12/5`
Answer:
`sin theta = 5/12`
`cos theta = 12/13`
`tan theta = 5/12`
`cosec theta =13/5`
`cot theta = 12/5`
Q6. If `angle A` and `angle B` are acute angles such that `cos A = cos B,` then show that
`angle A=angle B.`
Sol. :
`angle A ` and `angle B` are acute angles.
`cos A = cos B`
To Show:
`cos A = cos B`
Solve:
Let `triangle ABC`
`cos A = cos B`
`(AC)/(AB) = (BC)/(AB)`
`AC = BC`
`angle A = angle B` [Angle opposite to equal sides are equal.]
Proved.
Q7. If `cot theta=7/8,` evaluate:
i) `((1+sin theta)(1-sin theta))/((1+cos theta)(1-cos theta))`
ii) `cot^2 theta`
Sol. :
i)
`= ((1 + sin theta)(1 - sin theta))/((1 + cos theta)(1 - cos theta))` [`(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2`]
`= (1 - sin^2 theta)/(1 - cos^2 theta)`
`= (cos^2 theta)/(sin^2 theta)`
`= (cot theta)^2`
`= cot^2 theta`
`= (7/8)^2`
`=49/64`
Answer:
`=49/64`
ii)
`= cot^2 theta`
`= (cot theta)^2`
`= (7/8)^2`
`= 49/64`
Answer:
`= 49/64`
Q8. If `3cot A=4,` check whether `(1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)=cos^2 A-sin^2 A` or not.
Sol. :
`cot A = 4/3`
Solve:
Let `triangle ABC`
`cot A = 4/3 = (AB)/(BC)`
By Pythagoras theorem
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`AC^2 = (4)^2 + (3)^2`
`AC^2 = 16 + 9`
`AC^2 = 25`
`AC^2 = (5)^2`
`AC = 5`
To Prove:
`(1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)=cos^2 A-sin^2 A` or not.
Proof:
`LHS.`
`= (1- (BC)/(AB))^2/(1+(BC)/(AB))^2`
`= (1-(3/4)^2)/(1+(3/4)^2)`
`= (1-9/16)/(1+9/16)`
`= (7/16)/(25/16)`
`= 7/25`
`RHS.`
`= cos^2A-sin^2A`
`= ((AB)/(AC))^2-((BC)/(AC))^2`
`= (4/5)^2-(3/5)^2`
`= 16/5-9/25`
`= (16-9)/25`
`= 7/25`
`LHS = RHS`
Proved.
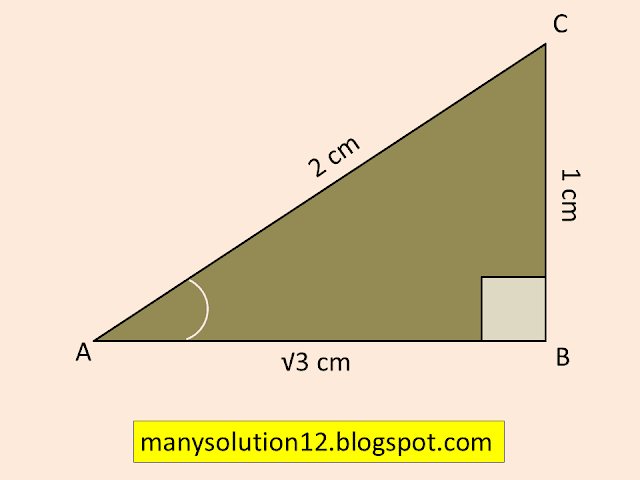
Q9. In triangle `ABC,` right-angled at `B,` if `tan A=1/sqrt3,` find the value of
i) `sin A cos C + cos A sin C`
ii) `cos A cos C - sin A sin C`
Sol. :
`tan A = 1/sqrt3`
Solve:
In `triangle ABC`
`tan A = 1/sqrt3 = (BC)/(AB)`
By Pythagoras theorem
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`AC^2 = (sqrt3)^2 + (1)^2`
`AC^2 = 3 + 1`
`AC^2 = 4`
`AC^2 = (2)^2`
`AC = 2`
i)
`= sin A cos C + cos A + sin C`
`= (BC)/(AC).(BC)/(AC) + (AB)/(AC).(AB)/(AC)`
`= ((BC)/(AC))^2 + ((AB)/(AC))^2`
`= (1/2)^2 + (sqrt3/2)^2`
`= 1/4 + 3/4`
`= 4/4 = 1`
Answer:
The value is `1`.
ii)
`= cos A cos C - sin A sin C`
`= (AB)/(AC).(BC)/(AC) - (BC)/(AC).(AB)/(AC)`
`= (AB.BC)/(AC)^2 - (AB.BC)/(AC)^2`
`= (sqrt3.1)/(2)^2 - (sqrt3.1)/(2)^2`
`= (sqrt3)/4 - (sqrt3)/4`
`= 0`
Answer:
The value is `0`.
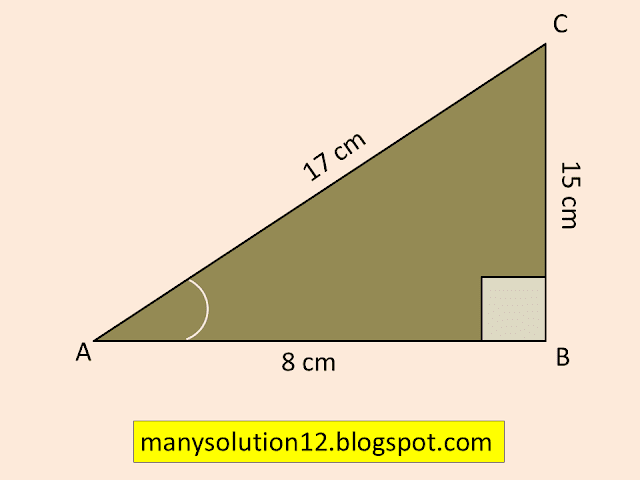
Q10. In `triangle PQR,` right-angled at `Q, PR+QR=25 cm` and `PQ=5 cm.` Determine the values of `sin P, cos P` and `tan P.`
Sol. :
`triangle PQR,` `angle Q = 90^circ, `
`PR + QR = 25 cm,`___________(1)
`PQ = 5 cm`.
To find:
`sin P, cos P,` and `tan P`.
Solve:
In `triangle PQR`
By Pythagoras theorem
`(PQ)^2 = (PR)^2 - (QR)^2`
`(5)^2 = (PR + QR)(PR - QR)`
`25 = 25(PR - QR)`
`25/25 = PR - QR`
`PR - QR = 1`____________(2)
From equation (1) `+` (2)
`PR + QR + PR - QR = 25 + 1`
`PR + PR = 26`
`2PR = 26`
`PR = 26/2`
`PR = 13`
Put in equation (1)
`13 + QR = 25`
`QR = 25 - 13`
`QR = 12`
`sin P = (QR)/(PR) = 12/13`
`cos P = (PQ)/(PR) = 5/13`
`tan P = (QR)/(QP) = 12/5`
Answer:
`sin P = 12/13, cos P = 5/13, tan P = 12/5`.
Q11. State whether the following are true or false, Justify your answer:
i) The value of `tan A` is always less than `1.`
ii) `sec A=12/5` for some value of angle `A.`
iii) `cos A` is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle `A.`
vi) `cot A` is the product of `cot` and `A.`
v) `sin theta=4/3` for some angle `theta.`
Answer:
i) false, ii) true iii) false iv) false v) false.



Comments