10th Maths 14.1
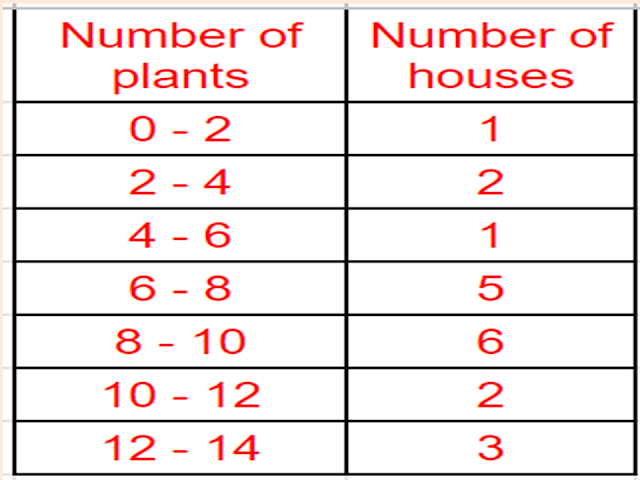
Chapter 14 Statistics NCERT Class 10th solution of Exercise 14.2 NCERT Class 10th solution of Exercise 14.3 NCERT Class 10th Maths Projects Exercise 14.1 Q.1 A survey was conducted by a group of students as a part of their environment awareness programme, in which they collected the following data regarding the number of plants in `20` houses in a locality. Find the mean number of plants per house. Which method did you use for finding the mean, and why? Sol. : `text {Mean } overline x = (∑f_ix_i)/(∑fi) = 162/20 = 8.1` `text {Answer:}` `8.1` plants. We have used direct method because numerical values of `x_i` and `f_i` are small. ☝ Like, Share, and Subscribe. Q2. Consider the following distribution of daily wages of `50` workers of a factory Find the mean daily wages of the workers of the factory by using an appropriate method. Sol. : `text{Let the assume mean a = 550 and h = 20` `text{Mean }overlinex = a + (∑f_iu_i)/(∑f_i)timesh` `= 550+(-12times20)/5...
